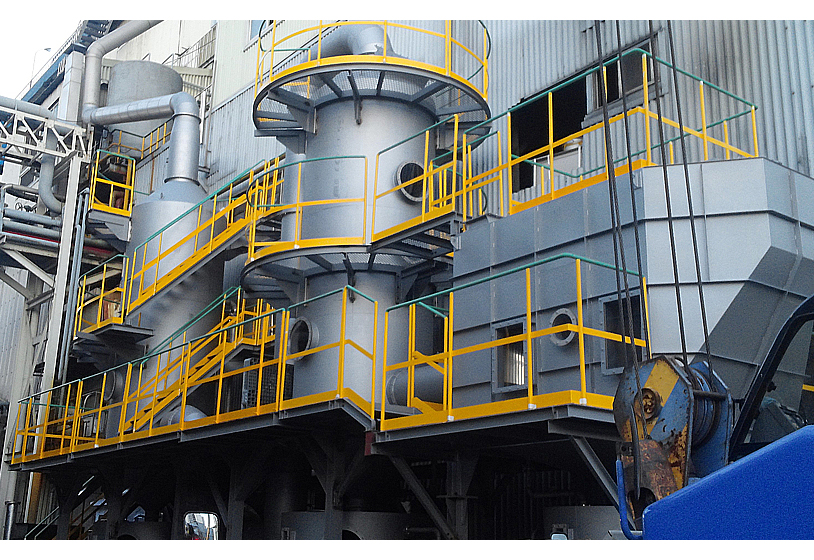
Air Pollution Control Plant
Air control Engineering Co., Ltd.
Scrubber ( Packing Tower )
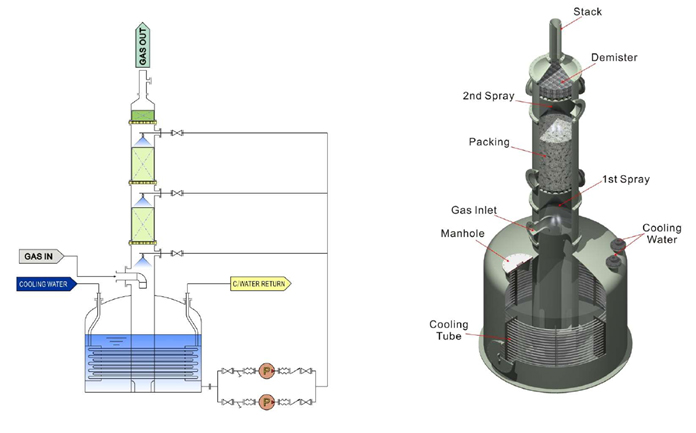
PROCESS DESCRIPTION
- The Packing Tower creates a thin layer of absorbent liquid (scrubbing liquid) over the packing material, allowing gas to come into contact and be absorbed.
- The absorbent liquid is sprayed by a liquid distribution device at the top of the packing layer and is recirculated by a circulation pump.
- Ultimately, it passes through a droplet separation device before being discharged into the atmosphere.
- The gas to be treated must be physically absorbed by the absorbent liquid or undergo a chemical reaction.
- The absorbent liquid may utilize substances such as acids/bases or oxidizing/reducing agents supplied through a chemical dosing system.
- As operations progress, it is necessary to supply fresh liquid and treat wastewater before reaching the gas-liquid equilibrium.
Characteristics
- Gas Velocity: 0.3~2.0 m/s
- Liquid-to-Gas Ratio: 1~20 ℓ/m3
- Packing Height: 0.5~5.0 m
- Pressure Loss: 10~50mmAq/m(packing height)
Advantages
- Maintains stable absorption efficiency despite fluctuations in gas flow.
- Low pressure loss leads to reduced power costs.
- Capable of design with high gas absorption efficiency.
Disadvantages
- Flooding limits operational velocity.
- Prone to clogging when handling gases with high solid content.
Applications
- Chemical plant
- Plating factory
- Wastewater treatment facility
- Night soil treatment facility
- Odor generating workplaces
- Hazardous Gas and VOC Emission Sites
Representative Pollutants and Absorbents
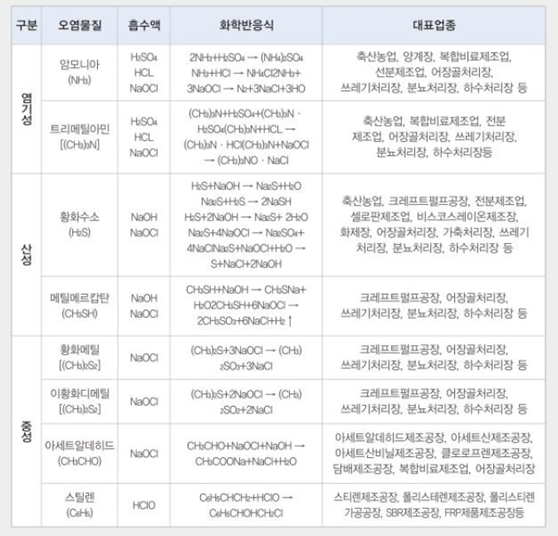
| Classification | Pollutant | Absorbent | Chemical Reaction | Representative Industries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | Ammonia (NH3) | H2SO4 HCL NaOCl |
2NH3+H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4 NH3+HCl → NH4Cl2NH3+ 3NaOCl → N2+3NaCl+3HO |
Livestock farming, poultry farms, compound fertilizer manufacturing, starch production, fishery waste treatment, waste disposal facilities, night soil treatment facilities, wastewater |
| rimethylamine [(CH3)3N] | H2SO4 HCL NaOCl |
(CH3)3N+H2SO4+(CH3)3N · H2SO4(CH3)3N+HCl → (CH3)3N · HCl(CH3)3N+NaOCl → (CH3)3NO · NaCl |
Livestock farming, compound fertilizer manufacturing, starch production, fishery waste treatment, waste disposal facilities, night soil treatment facilities, wastewater treatment plants, etc. | |
| Acidic | Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) | NaOH NaOCl |
H2S+NaOH → Na2S+H2O Na2S+H2S → 2NaSH H2S+2NaOH → Na2S+2H2O Na2S+4NaOCl → Na2SO4+ 4NaCl Na2S+NaOCl+H2O → S+NaCl+2NaOH |
Livestock farming, kraft pulp mills, starch manufacturing, cellophane production, viscose rayon manufacturing, chemical plants, fishery waste treatment, leather processing plants, waste disposal facilities, night soil treatment facilities, wastewater treatment facilities, etc. |
| Methyl Mercaptan (CH3SH) | NaOH NaOCl |
CH3SH+NaOH → CH3SNa+ H2O2CH3SH+6NaOCl → 2CH3SO3+6NaCl+H2 ↑ |
Kraft pulp mills, fishery waste treatment facilities, waste disposal facilities, night soil treatment facilities, wastewater treatment facilities, etc. | |
| Neutral | Dimethyl Disulfide [(CH3)2S] | NaOCl | (CH3)2S+3NaOCl → (CH3) 2SO3+3NaCl |
Kraft pulp mills, fishery waste treatment facilities, waste disposal facilities, night soil treatment facilities, wastewater treatment facilities, etc. |
| Dimethyl Disulfide [(CH3)2S2] | NaOCl | (CH3)2S+2NaOCl → (CH3) 2SO2+2NaCl |
Kraft pulp mills, fishery waste treatment facilities, waste disposal facilities, night soil treatment facilities, wastewater treatment facilities, etc. | |
| Acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) | NaOCl | CH3CHO+NaOCl+NaOH → CH3COONa+NaCl+H2O |
Acetaldehyde production plants, acetic acid production plants, polyvinyl acetate production plants, chloroprene production plants, tobacco manufacturing plants, compound fertilizer manufacturing, fishery waste treatment facilities. | |
| Styrene (C6H5) | HClO | C6H5CHCH2+HClO → C6H5CHOHCH2Cl |
Styrene manufacturing plants, polystyrene manufacturing plants, polystyrene processing plants, SBR manufacturing plants, FRP product manufacturing facilities. |
Material of Scrubber
- PVC + FRP: Good durability, lightweight, and cost-effective, but lower chemical resistance than FRP.
- FRP: Good chemical resistance (vulnerable to sulfuric acid), but weak against impacts.
- STS: Excellent chemical resistance and durability.
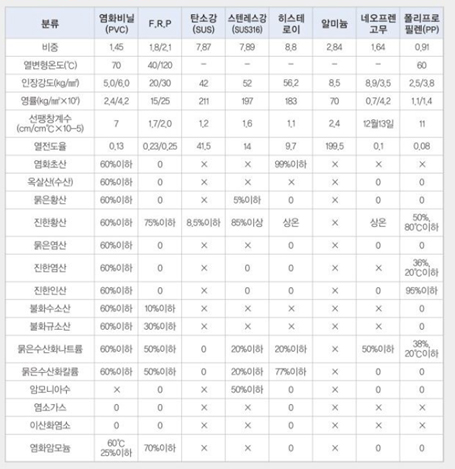
| Classification | F.R.P | Carbon Steel (SS41) |
Stainless Steel (SUS316) |
Hastelloy C | Aluminum | PVC | Neoprene Rubber |
Polypropylene (PP) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.8/2.1 | 7.87 | 7.89 | 8.80 | 2.84 | 1.45 | 1.64 | 0.19 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Distortion Temp(℃) | 40/120 | - | - | - | - | 70 | - | 60 |
| Tensile Strength(㎏/㎟) | 20/30 | 42 | 52 | 56.2 | 8.5 | 5.0/6.0 | 8.9/3.5 | 2.5/3.8 |
| Modulus(㎏/㎟×10²) | 15/25 | 211 | 197 | 18.3 | 70 | 2.4/4.2 | 0.7/4.2 | 1.1/1.4 |
| Coefficient of Linear Expansion (㎝/㎝ ℃× 10⁻⁵) |
1.7/2.0 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 2.4 | 7.0 | 12/13 | 11.0 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.23/0.25 | 41.5 | 14.0 | 9.7 | 199.5 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.08 |
| Acetic Acid | 0 | x | x | 99% or more | x | 60% or less | x | x |
| Oxalic Acid(Water) | 0 | x | x | x | x | 60% or less | o | o |
| Dilute Sulfuric Acid | 0 | x | 5% or less | o | x | 60% or less | o | o |
| Concentrated Sulfuric Acid | 75% or less | 8.5% or less | 85% or more | Room temp | x | 60% or more | Room temp | 80℃,50% or more |
| Dilute Hydrochloric Acid | 0 | x | x | o | x | 60% or less | o | o |
| Concentrated Hydrochloric Acid | 0 | x | o | o | x | 60% or less | x | 20℃,36% or less |
| Concentrated Phosphoric Acid | 0 | x | o | o | x | 60% or less | o | 95% or less |
| Hydrofluoric Acid | 10 or less | x | x | x | x | 60% or less | x | o |
| Silicofluoric Acid | 30% or less | x | x | x | x | 60% or less | x | o |
| Dilute Sodium Hydroxide | 50% or less | 0 | 20% or less | 20% or less | x | 60% or less | 50% or less | 20℃,38% or less |
| Dilute Potassium Hydroxide | 50% or less | 0 | 20% or less | 77% or less | x | 60% or less | o | o |
| Ammonium Hydroxide | 0 | - | 50% or less | 0 | x | x | o | o |
| Chlorine Gas | 0 | x | x | 0 | x | o | x | x |
| Chlorine Dioxide | 0 | x | x | 0 | x | o | x | x |
| Ammonium Chloride | 70% or less | x | x | 0 | x | 60℃,25% or less | o | o |
Types of Packing Materials

Raschig Ring

Spirax
Pall Ring

Intalox Saddle

Berl Saddle
Lessing Ring
Cross Ring
S-Spiral Ring
D-Spiral Ring
T-Spiral Ring
Inter Pack
Net Ring
Dixson Pack

Mcmahon Pack
Canon Pack

Stedman Pack

Goodlow Racking
Heilex
Pana Pack
Wooden Grid
Conditions for Packing Materials
- High surface area per unit volume
- Uniform distribution of gas and liquid
- Corrosion resistance for both gas and liquid
- Low pressure loss and high packing density
- Sufficient chemical resistance
- Low corrosiveness to target substances
- Minimal hold-up of the cleaning liquid
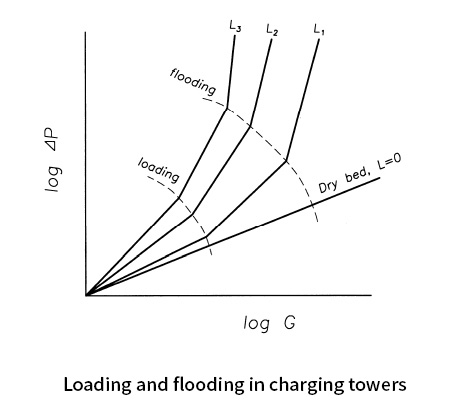
Breakthrough Point of Packing Tower
- The phenomenon where the cleaning liquid does not flow down due to gravity but remains within the packing layer, leading to increased pressure loss and decreased treatment efficiency. This occurs more significantly with faster gas flow rates, higher viscosity of the cleaning liquid, and greater load pressure on the packing material.
- Loading Point: The first breakthrough point where the hold-up of the cleaning liquid increases, causing a sudden change in pressure loss and the descent speed of the cleaning liquid.
- Flooding Point: The second breakthrough point where excessive gas flow causes the cleaning liquid to overflow, making downstream operations impossible.
- For smooth scrubber operation, it is recommended to operate at 40-70% of the maximum flooding point.
Application Case(CJ CheilJedang 100HP)

